Oral disease is a serious public health problem globally. In Rwanda, dental caries and periodontal disease are among the most important causes of morbidity and are on the top ten causes of consultations at primary and secondary levels of healthcare system (R- HMIS –Data Base 2016).
Findings of the National Oral Health Survey of Rwanda Draft Report 2017 show that 50% of children aged 2-5 years have untreated dental problems, and their impact on nutrition and growth is considerable.
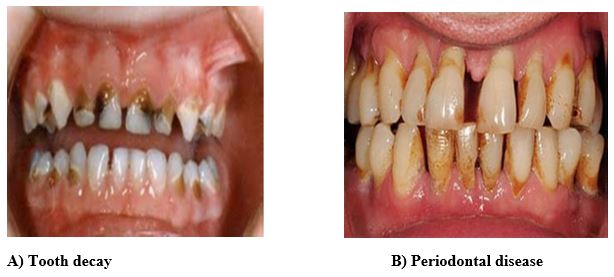
Although tooth decay, gum diseases and oral cancer are preventable and have similar risk factors with diabetes, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases as well as obesity and oral cancer (NCDs), national attention to oral diseases does not match the high number of cases and the impact these diseases have on individuals and society.
Tooth decay and gum disease are a menace to overall health, causing intense pain and discomfort; and can prevent people from having enjoyable and productive life.
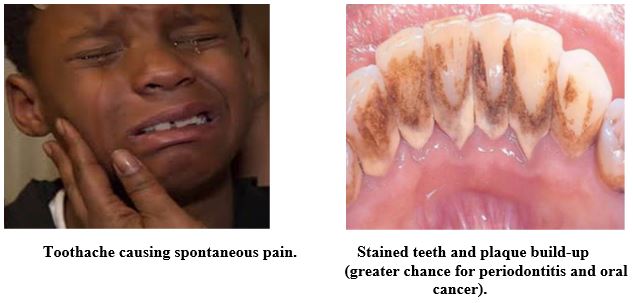
Children in particular, toothache and tooth loss can lead to speech and language development problems and can be a source of malnutrition, distraction from play and learning.




